Optical fiber is extremely important in today’s digital age
Optical fiber is the unsung hero that is responsible for the digital age.
Optical fiber is extremely important in today’s digital age, when rapid and secure communication is required for a wide range of activities, including banking, education, entertainment, and healthcare, but it is not well recognized. The internet, phone lines, and other forms of digital infrastructure are all made possible by these minuscule pieces of glass or plastic that are widely distributed around the globe.
But what exactly is an optical fiber? This is how it operates. To what extent do a lot of individuals believe that this is the most effective technique to converse quickly?
An investigation into the science, engineering, applications, and promise for the future of this novel technology is warranted.
Describe what a fiber optic is.
A fiber optic, also known as an optical fiber, is a strand of glass (silica) or plastic that is just a tiny bit thicker than a hair and is extremely thin and flexible. Because it transmits data in the form of light pulses, it enables you to communicate with individuals at a very rapid pace and over extensive distances.
The fact that fiber optics makes use of light rather than electricity enables it to be more reliable, faster, and capable of transmitting a greater amount of data.
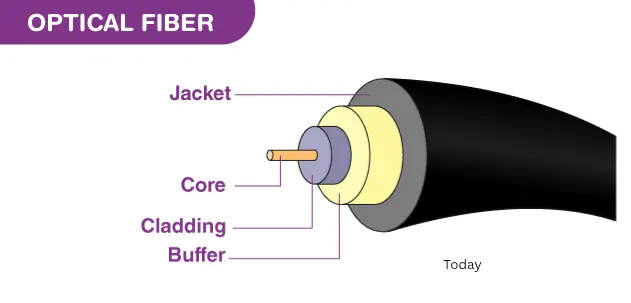
The components that make up an optical fiber
Every optical fiber is composed of three primary layers:
The core
The portion that allows the greatest amount of light to pass through.
Glass or material that is extremely transparent in appearance.
Between 8 to 62.5 µm is the average size of the particles.
Cladding (cladding)
The signal is prevented from escaping the core by this.
Protective covering or a jacket for the buffer
A protective coating that is installed on the exterior.
Safeguards the fiber against the effects of moisture, damage from the environment, and stress from the surrounding environment.
Internal Reflection in its Totality
To put it simply, this is the essence of fiber optics. As a result of light signals being reflected off of the cladding at shallow angles, they are prevented from leaving the core and are able to travel the greatest distance possible.
What is the operation of fiber optics?
The procedure begins with a light source that is either a laser or an LED. Specifically, it converts electrical signals, like as data from a phone or the internet, into light pulses. After then, the pulses are sent by the optical fiber. The light pulses are converted back into electrical impulses by a photodetector, which is located at the opposite end.
As a result of the fact that this entire process takes place at speeds that are nearly identical to the speed of light, people are able to communicate with one another in a manner that is essentially instantaneous across cities, countries, and oceans.
There are numerous varieties of optical fibers.
1. Single-mode fiber (SMF), also known as single-mode fiber
About 8 to 10 micrometers is the diameter of the core.
A single ray of light is brought in
Optimal for transmitting data over extensive distances (more than one hundred kilometers).
Utilized in the construction of cables for long-distance networks, transmissions, and submarines.
2. Multi-Mode Fiber, often known as MM
The core has a diameter that ranges from 50 to 62.5 micrometers.
More than one light path can be held at the same time.
Applicable to short trips (up to two kilometers)
Utilized in local area networks (LANs), data centers, and surveillance systems.
Things that are positive about optical fiber
1. Sending in a hurry
Data can be transmitted at speeds of up to one hundred gigabits per second (Gbps), which is far faster than copper lines.
2. An increase in bandwidth
Due to the fact that fiber connections are capable of moving a significant amount of data, they are ideal for activities such as video calling, streaming, and accessing the cloud.
3. Protection across extremely long distances
When there are fewer repeaters and operations that are more dependable, there is less signal loss over longer distances.
4. preventing meddling from occurring
Radio frequency interference (RFI) and electromagnetic interference (EMI) do not cause any damage to optical fiber, in contrast to copper, which is susceptible to its effects.
5. Five, safer
Because it is difficult to tap into fiber without being discovered, the military, the government, and banks are all interested in it.
6. Not hefty or large in size
Because they are more lightweight and thinner than copper wires, it is much simpler to install and move them from one location to another.
7. Conserves energy
In comparison to copper systems, it does not consume as much power, which is beneficial to the environment.
Functions of Optical Fiber
Telecommunications Services
The primary method by which information is transmitted between mobile networks, the internet, and the rest of the population of the world.
Internet at Home (FTTH/FTTP) connections
The Fiber to the Home initiative offers lightning-fast and dependable internet to people’s homes, which in turn revolutionizes the ways in which they work, play games, and stream content.
The provision of medical care
Because of its precision and adaptability, it finds applications in medical equipment like as endoscope, laser surgery, and sensors.
The fields of Aerospace or Defense
It enables military bases, drones, submarines, and aircraft to communicate with one another in a secure and expedient manner.
Radio and Television Broadcasting
Real-time transmission of audio and video of a high quality can be accomplished anywhere in the world on this platform.
The Internet of Things and Smart Cities will be discussed.
Important pieces of smart city infrastructure equipment, such as cameras, sensors, and traffic systems, can be connected to one another through fiber networking.
How the World Will Be Changed by Fiber Optics
There are more than 5 billion kilometers of optical fiber that connect locations all over the world, including areas that are submerged in oceans, over deserts, through forests, and even inside enormous buildings.
There are cables in the water.
People from all over the world are able to engage in commerce, communicate with one another, and make use of digital services thanks to the submarine fiber-optic cables that connect continents. Over ninety-nine percent of all internet traffic between countries is carried by these cables.
In low-income countries
Countries in Africa, Asia, and South America are rapidly expanding their fiber networks in an effort to bridge the digital gap and stimulate economic growth.
Optical fiber’s future as a technology
It is likely that fiber optics will undergo even more transformations as we go into a new era that includes 5G, artificial intelligence, augmented reality and virtual reality, and quantum computing.
Keep an eye out for the following:
Due to the fact that light passes through air at a higher rate than it does through glass, almost no data is lost during the transmission process when using hollow-core fibers.
For networks in homes and cars that are only a short distance apart, Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) is a more flexible and cost-effective option than other types of connections.
The use of quantum key distribution (QKD) in quantum fiber networks renders it hard for hackers to get access to communications infrastructure.
Due to the fact that 5G towers require fiber backhaul in order to maintain an extremely low latency, they utilize both fiber and wireless.
Facts that are fun to know
While traveling through fiber, light signals can reach speeds of up to 200,000 kilometers per second, which is equivalent to two-thirds of the speed of light in a vacuum.
More than 25,000 high-definition video streams can be transmitted simultaneously over a single strand of fiber.
Certain fiber cables have the potential to last for more than 25 years
end.
It is optical fiber that enables the data highways of our modern world to function, from the data highways of your smartphone to the data highways of space exploration. This technology is essential for the development of digital communication in the future since it is more dependable than wireless and faster than copper.
এটা
Optical fiber is the foundation for everything you do, including streaming,
gaming, making phone calls, studying, and working with code.
As a final word,
world in which everything is interconnected, optical fiber serves as the invisible thread that provides the connection between everything.
Share this content: